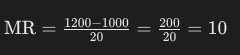Understanding the intricacies of marginal revenue is crucial for businesses aiming to maximize their profits and optimize pricing strategies. This comprehensive guide will delve into what marginal revenue is, how to calculate it, and the significance of the marginal revenue formula. By mastering these concepts, you’ll gain valuable insights into the financial health of your business and make informed decisions that drive growth.
On this page, we’ll break down the marginal revenue equation, providing step-by-step instructions on how to find and solve it. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking to refine your knowledge, this guide offers practical examples and applications to help you understand and leverage marginal revenue effectively. From exploring its role in different market structures to debunking common misconceptions, our goal is to equip you with the tools and knowledge needed to harness the power of marginal revenue in your business endeavors.
Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional income generated from the sale of one more unit of a good or service. It is a critical concept in economics and business because it helps companies understand how revenue changes with varying levels of output. Marginal revenue is essential for making informed decisions about production and pricing strategies, as it directly impacts profit maximization.
How to Calculate Marginal Revenue
Calculating marginal revenue involves determining the change in total revenue that results from selling an additional unit. The formula for marginal revenue is straightforward:
Where:
- ΔTotal Revenue- is the change in total revenue.
- ΔQuantity- is the change in the number of units sold.
For example, if a company’s total revenue increases from $1,000 to $1,200 when it sells an additional 20 units, the marginal revenue would be calculated as follows:
This means the marginal revenue for each additional unit sold is $10.
Finding and Using the Marginal Revenue Formula
To find marginal revenue, businesses must track changes in their total revenue as they adjust their output levels. This requires accurate record-keeping and analysis of sales data. Once the marginal revenue is determined, companies can use this information to make strategic decisions.
For instance, if the marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost (the cost of producing one more unit), the company should increase production to maximize profits. Conversely, if the marginal revenue is less than the marginal cost, reducing production may be more beneficial.
Practical Applications of Marginal Revenue
Understanding and applying the marginal revenue formula is essential for effective pricing strategies. By knowing how much additional revenue each unit generates, businesses can set prices that optimize their revenue. This is particularly important in competitive markets, where pricing decisions can significantly impact market share and profitability.
Moreover, marginal revenue analysis can help businesses identify the optimal output level, where profits are maximized. This involves comparing marginal revenue with marginal cost to ensure that each unit produced contributes positively to the overall profit.
In conclusion, mastering the concept of marginal revenue provides businesses with the tools needed to make informed production and pricing decisions. By calculating and analyzing marginal revenue, companies can enhance their financial performance and achieve sustainable growth.
Using Marginal Revenue To Determine Success
Marginal revenue is a powerful metric that provides valuable insights into a business’s performance and potential for success. By analyzing marginal revenue, companies can make informed decisions that drive profitability and growth. Here are several ways marginal revenue can be used to determine success:
Assessing Profitability
One of the primary uses of marginal revenue is to assess the profitability of additional production. When a business understands the revenue generated by each additional unit sold, it can compare this figure with the marginal cost of production. If marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, the business is operating profitably for those additional units. This comparison helps determine whether increasing or decreasing production will enhance overall profitability.
Optimizing Pricing Strategies
Marginal revenue is crucial for developing effective pricing strategies. By examining how revenue changes with different levels of output, businesses can identify the optimal price point that maximizes revenue. This involves understanding the relationship between price, demand, and revenue. For instance, if lowering the price slightly increases the quantity sold significantly, resulting in higher overall revenue, the business can adjust its pricing strategy accordingly.
Making Investment Decisions
In competitive markets, understanding marginal revenue helps businesses make strategic decisions to stay ahead of competitors. Companies can use marginal revenue data to fine-tune their product offerings, marketing efforts, and pricing strategies. By focusing on the most profitable segments and adjusting production levels to meet market demand, businesses can maintain a competitive edge and improve their market position.
Enhancing Market Competitiveness
Marginal revenue analysis can guide investment decisions by highlighting the potential returns on new projects or expansions. By estimating the additional revenue generated from investing in new equipment, technology, or product lines, businesses can evaluate whether these investments will contribute positively to their financial performance. This approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively to projects that offer the highest potential for success.
The Bottom Line
Understanding and leveraging marginal revenue is essential for businesses aiming to maximize their profitability and strategic decision-making. By accurately calculating and analyzing marginal revenue, companies can make informed choices about production levels, pricing strategies, and investment opportunities. This not only enhances their financial performance but also positions them for sustained success in a competitive market.
Marginal revenue provides critical insights into how each additional unit sold impacts total revenue, enabling businesses to fine-tune their operations and optimize resource allocation. Whether you are assessing profitability, enhancing market competitiveness, or planning for future growth, marginal revenue serves as a vital tool in your business arsenal.
By incorporating the principles and practices discussed in this guide, businesses can achieve greater clarity and precision in their financial planning and execution. The bottom line is that mastering marginal revenue empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions that drive growth, efficiency, and long-term success.